Breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) for an extended time can have fatal results because it is a poisonous gas. Carbon monoxide is the resulting gas from burning coal, gas, wood, and oil in a confined space. Installing a carbon monoxide alarm can help prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Carbon monoxide poisoning causes include:
- Breathing motor vehicle exhaust fumes in a confined space
- Inhaling the smoke from burning warming or cooking materials, e.g., wood, coal, gas, and oil, in a confined space
- Breathing in smoke from a blocked chimney flue
- Defective gas or paraffin heater emissions
Treating Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
When someone breathes in carbon monoxide, the gas binds with the blood’s hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen through the body) and starves it of oxygen. It is called carboxyhemoglobin (COHb).
Signs and Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Exposure at low levels may cause:
- Headaches
- Confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurry vision
- Irregular heartbeat
- Aggression
Exposure at high levels may cause:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Changes in skin coloration (cherry-red or grey-blue)
- Reduced levels of response, including unresponsiveness
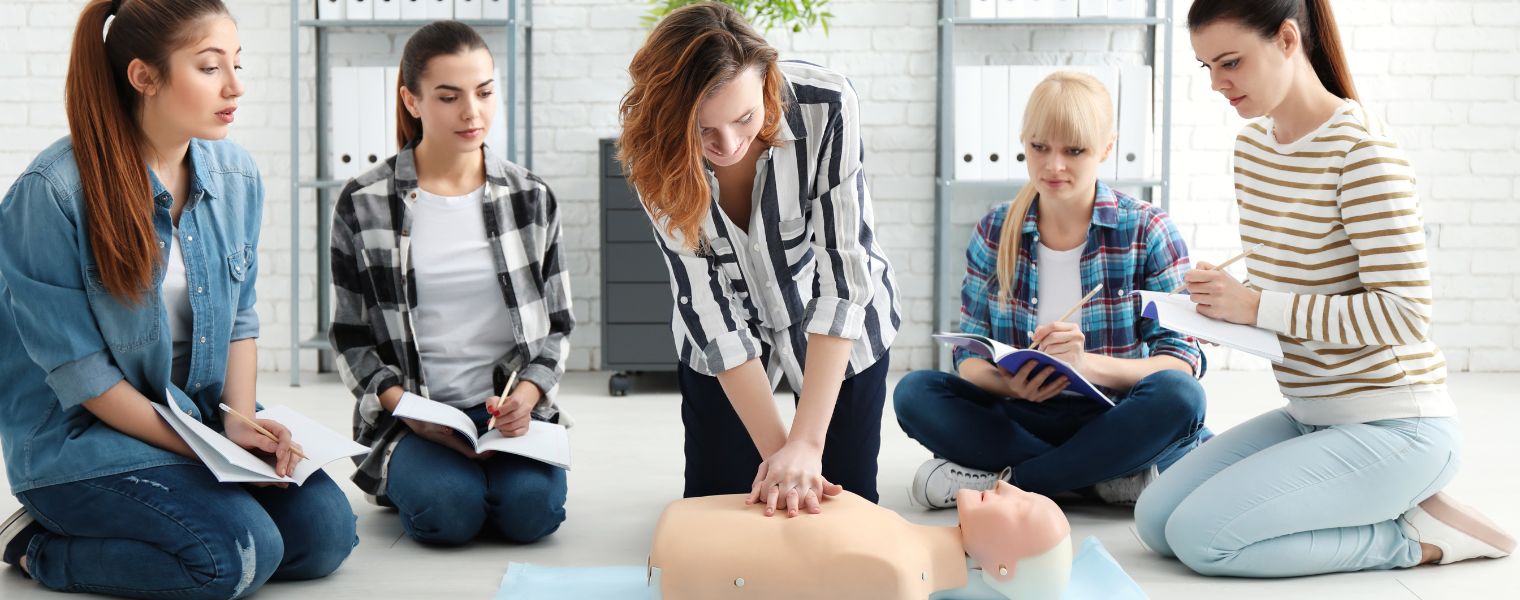
Inquire about First Aid & CPR Training Course
Certify for First Aid training learn skills that increase their confidence and willingness to respond to others in a crisis as you complete the course with us. Call our toll-free number to know more.
Providing First Aid Treatment
If you suspect someone has CO poisoning, remember it is a life-threatening emergency.
You must immediately remove them from the confined space and take them outside for exposure to some fresh air. If you can, do this without entering the room yourself. If you know where to and can quickly and safely turn off the source of the carbon monoxide, then do it if needed to keep you and the victim of CO poisoning safe.
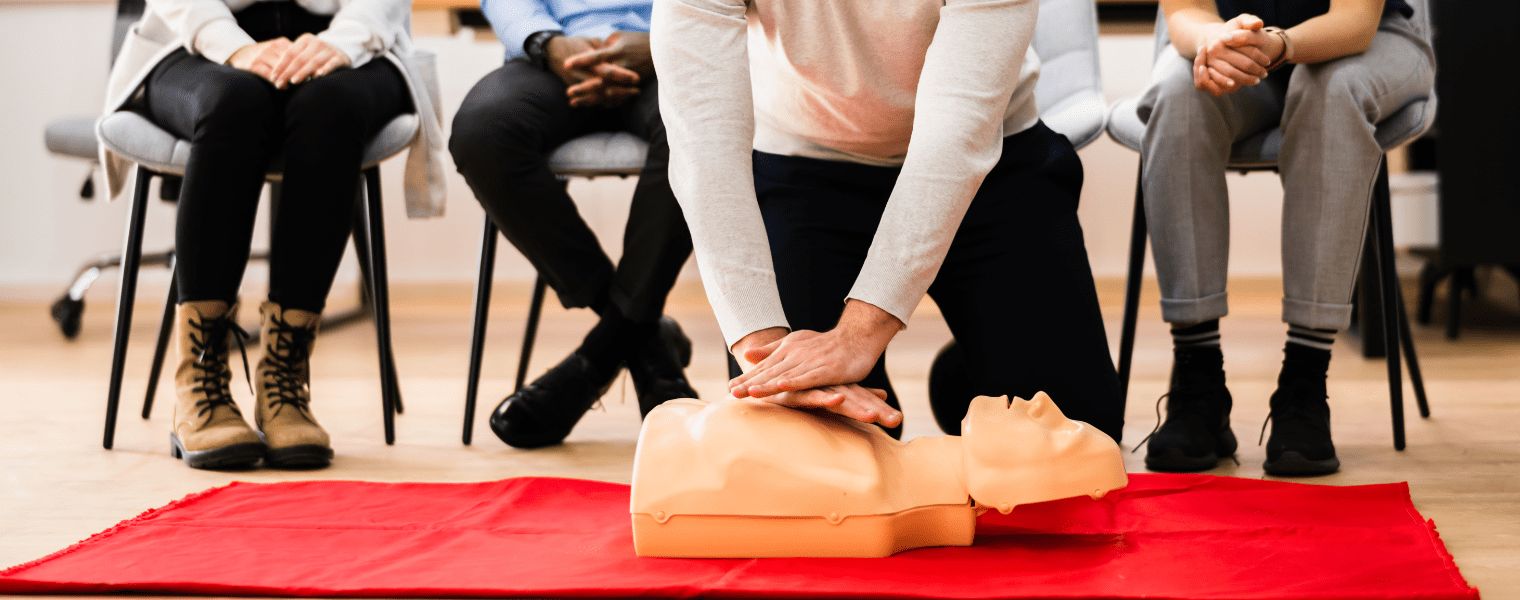
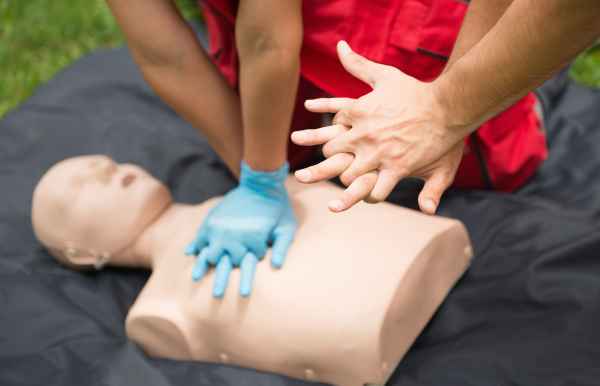
If the person is not breathing, you must immediately start CPR and continue until they can breathe independently. If you have someone with you, ask them to call 911. You can alternate performing CPR on the person as long as needed or until paramedics arrive.
However, if you’re alone, do CPR for two minutes, call 911, and then continue until the person can breathe or emergency help arrives.
Stay with the person until help arrives, but keep monitoring their vital signs, breathing, and response levels.

FAQ on Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Oxygen therapy is the best way to treat carbon monoxide poisoning. Once paramedics arrive on the scene, they will apply an oxygen mask, and the person will get several hours of pure oxygen therapy once they arrive at a hospital emergency room to ensure that the carbon monoxide is completely removed from the bloodstream.
Here are questions people frequently ask about carbon monoxide poisoning:
How can you rid the body of carbon monoxide?
A CO poisoning diagnosis means that the most effective way to rid the body of carbon monoxide is by giving them treatment with 100% oxygen as soon as possible.
The best ways to force carbon monoxide from the body and replace it with oxygen include:
- Providing continuous airway pressure (CPAP)
- Using an oxygen mask with a valve
- Administering oxygen through a reservoir mask with 15 liters per minute.
How long before the body’s carbon monoxide levels reduce?
A person with carbon monoxide poisoning requires between four and a half to five hours of breathing natural air to reduce CO by half. The time needed to clear the body entirely with 100% oxygen is an hour and a half. When treated with three atmospheres of air pressure in a hyperbaric chamber, it takes about 20 minutes to replenish the oxygen levels.
However, doctors will continue the oxygen treatment until the blood levels of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) drop to less than 3%, and all symptoms of the CO poisoning have abated.

What can happen if carbon monoxide poisoning is left untreated?
Carbon monoxide poisoning has a cumulative effect, meaning that the symptoms will depend on the time the CO exposure occurred and how long it remained in the bloodstream.
Therefore, brief exposure to a small amount of CO may only mean that the person suffers from nausea and headache. However, lengthy exposure to a more significant amount of CO can lead to more severe problems for the victim. These include shortness of breath, changes in mental alertness, neurological issues, unresponsiveness, and death.
Is carbon monoxide poisoning always lethal?
No, but unless CO poisoning is detected and treated immediately, it can cause permanent damage to the victim.
When the levels of COHb in the blood reach 60% or more, the person has a high risk of dying. Additionally, CO poisoning damages the heart and increases the risk of death for the victim over the next ten years.
Even in cases where CO poisoning isn’t fatal, the person can have resulting symptoms for several days or weeks after exposure. These include problems with their vision, abdominal pain, and some neurologic symptoms.
Ways to Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Besides installing carbon monoxide detectors in all areas where you have appliances that burn fuel, here are some other ways to prevent anyone from suffering from carbon monoxide poisoning:
- Check all furnaces, water heaters, gas ovens, wood stoves, and other fuel-burning appliances annually.
- Inspect and clean fireplaces each year.
- When using fuel-burning space heaters, make sure you have a well-ventilated space.
- Don’t start up or let the engine idle on gas lawn mowers, cars, trucks, or other vehicles in enclosed areas like your garage, even when the doors are open.
- Always try to vent fuel-burning appliances outside whenever possible.
- Never use charcoal grills in areas without ventilation, including your home, garage, tent, or camper van.
- Never use portable heaters or lanterns in enclosed areas, such as tents, campers, etc., while sleeping. The CO poisoning risk increases at high altitudes, so keep this in mind when camping.
- Never use a gas oven as a heating source for your home.
- If you use a gas-powered generator for electricity, always keep it far from your home.

Importance of First Aid Training for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
First aid training gives you the skills to act quickly and decisively with carbon monoxide poisoning in the workplace or at home. Choose a Coast2Coast First Aid & CPR course today in any of our centers and get your WSIB-approved Red Cross Certification that can help you save a life.